PPP (with BM3D) Image Deconvolution (ADMM Solver)#
This example demonstrates the solution of an image deconvolution problem using the ADMM Plug-and-Play Priors (PPP) algorithm [50], with the BM3D [16] denoiser.
[1]:
import numpy as np
from xdesign import Foam, discrete_phantom
import scico.numpy as snp
from scico import functional, linop, loss, metric, plot, random
from scico.optimize.admm import ADMM, LinearSubproblemSolver
from scico.util import device_info
plot.config_notebook_plotting()
Create a ground truth image.
[2]:
np.random.seed(1234)
N = 512 # image size
x_gt = discrete_phantom(Foam(size_range=[0.075, 0.0025], gap=1e-3, porosity=1), size=N)
x_gt = snp.array(x_gt) # convert to jax array
Set up forward operator and test signal consisting of blurred signal with additive Gaussian noise.
[3]:
n = 5 # convolution kernel size
σ = 20.0 / 255 # noise level
psf = snp.ones((n, n)) / (n * n)
A = linop.Convolve(h=psf, input_shape=x_gt.shape)
Ax = A(x_gt) # blurred image
noise, key = random.randn(Ax.shape)
y = Ax + σ * noise
Set up ADMM solver.
[4]:
f = loss.SquaredL2Loss(y=y, A=A)
C = linop.Identity(x_gt.shape)
λ = 20.0 / 255 # BM3D regularization strength
g = λ * functional.BM3D()
ρ = 1.0 # ADMM penalty parameter
maxiter = 10 # number of ADMM iterations
solver = ADMM(
f=f,
g_list=[g],
C_list=[C],
rho_list=[ρ],
x0=A.T @ y,
maxiter=maxiter,
subproblem_solver=LinearSubproblemSolver(cg_kwargs={"tol": 1e-3, "maxiter": 100}),
itstat_options={"display": True},
)
Run the solver.
[5]:
print(f"Solving on {device_info()}\n")
x = solver.solve()
x = snp.clip(x, 0, 1)
hist = solver.itstat_object.history(transpose=True)
Solving on GPU (NVIDIA GeForce RTX 2080 Ti)
Iter Time Prml Rsdl Dual Rsdl CG It CG Res
------------------------------------------------------
0 7.79e+00 9.643e+00 1.472e+01 3 2.084e-04
1 1.42e+01 3.772e+00 9.269e+00 3 2.291e-04
2 2.01e+01 1.408e+00 6.593e+00 2 6.981e-04
3 2.59e+01 1.081e+00 4.910e+00 2 4.567e-04
4 3.18e+01 9.272e-01 3.868e+00 2 3.328e-04
5 3.76e+01 8.377e-01 3.187e+00 2 2.492e-04
6 4.35e+01 7.924e-01 2.704e+00 2 1.942e-04
7 4.93e+01 6.816e-01 2.305e+00 1 9.075e-04
8 5.50e+01 7.081e-01 2.061e+00 1 6.446e-04
9 6.08e+01 6.930e-01 1.859e+00 1 6.303e-04
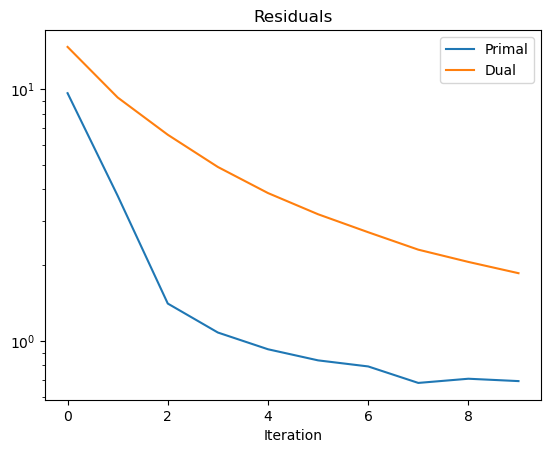
Show the recovered image.
[6]:
fig, ax = plot.subplots(nrows=1, ncols=3, figsize=(15, 5))
plot.imview(x_gt, title="Ground truth", fig=fig, ax=ax[0])
nc = n // 2
yc = snp.clip(y[nc:-nc, nc:-nc], 0, 1)
plot.imview(y, title="Blurred, noisy image: %.2f (dB)" % metric.psnr(x_gt, yc), fig=fig, ax=ax[1])
plot.imview(x, title="Deconvolved image: %.2f (dB)" % metric.psnr(x_gt, x), fig=fig, ax=ax[2])
fig.show()
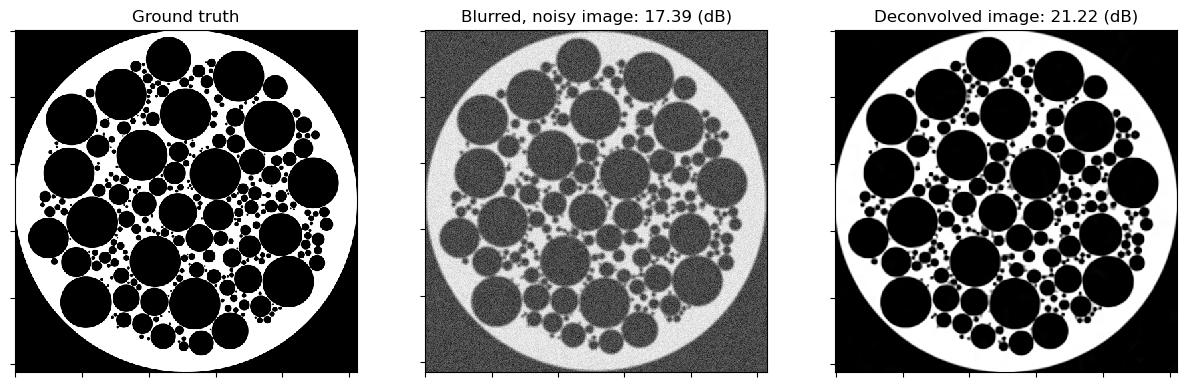
Plot convergence statistics.
[7]:
plot.plot(
snp.vstack((hist.Prml_Rsdl, hist.Dual_Rsdl)).T,
ptyp="semilogy",
title="Residuals",
xlbl="Iteration",
lgnd=("Primal", "Dual"),
)