Circulant Blur Image Deconvolution with TV Regularization#
This example demonstrates the solution of an image deconvolution problem with isotropic total variation (TV) regularization
\[\mathrm{argmin}_{\mathbf{x}} \; (1/2) \| \mathbf{y} - A \mathbf{x}
\|_2^2 + \lambda \| C \mathbf{x} \|_{2,1} \;,\]
where \(A\) is a circular convolution operator, \(\mathbf{y}\) is the blurred image, \(C\) is a 2D finite difference operator, and \(\mathbf{x}\) is the deconvolved image.
[1]:
from xdesign import SiemensStar, discrete_phantom
import scico.numpy as snp
import scico.random
from scico import functional, linop, loss, metric, plot
from scico.optimize.admm import ADMM, CircularConvolveSolver
from scico.util import device_info
plot.config_notebook_plotting()
Create a ground truth image.
[2]:
phantom = SiemensStar(32)
N = 256 # image size
x_gt = snp.pad(discrete_phantom(phantom, N - 16), 8)
Set up the forward operator and create a test signal consisting of a blurred signal with additive Gaussian noise.
[3]:
n = 5 # convolution kernel size
σ = 20.0 / 255 # noise level
psf = snp.ones((n, n)) / (n * n)
A = linop.CircularConvolve(h=psf, input_shape=x_gt.shape)
Ax = A(x_gt) # blurred image
noise, key = scico.random.randn(Ax.shape, seed=0)
y = Ax + σ * noise
Set up an ADMM solver object.
[4]:
λ = 2e-2 # L21 norm regularization parameter
ρ = 5e-1 # ADMM penalty parameter
maxiter = 50 # number of ADMM iterations
f = loss.SquaredL2Loss(y=y, A=A)
# Penalty parameters must be accounted for in the gi functions, not as
# additional inputs.
g = λ * functional.L21Norm() # regularization functionals gi
C = linop.FiniteDifference(x_gt.shape, circular=True)
solver = ADMM(
f=f,
g_list=[g],
C_list=[C],
rho_list=[ρ],
x0=A.adj(y),
maxiter=maxiter,
subproblem_solver=CircularConvolveSolver(),
itstat_options={"display": True, "period": 10},
)
Run the solver.
[5]:
print(f"Solving on {device_info()}\n")
x = solver.solve()
hist = solver.itstat_object.history(transpose=True)
Solving on GPU (NVIDIA GeForce RTX 2080 Ti)
Iter Time Objective Prml Rsdl Dual Rsdl
-----------------------------------------------
0 1.31e+00 2.706e+02 8.268e+00 6.982e+00
10 2.41e+00 2.773e+02 4.006e-01 1.662e+00
20 2.47e+00 2.754e+02 1.668e-01 9.856e-01
30 2.53e+00 2.746e+02 9.411e-02 6.923e-01
40 2.60e+00 2.742e+02 6.486e-02 5.095e-01
49 2.65e+00 2.740e+02 4.885e-02 4.005e-01
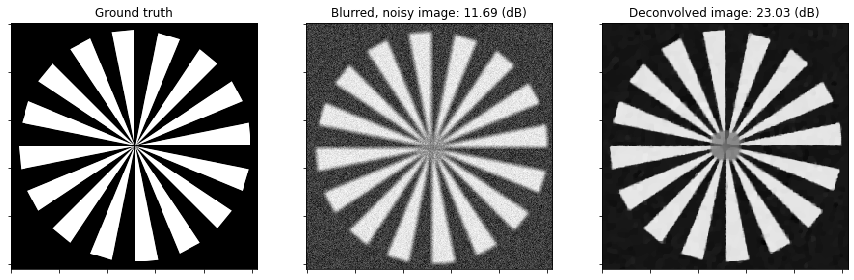
Show the recovered image.
[6]:
fig, ax = plot.subplots(nrows=1, ncols=3, figsize=(15, 5))
plot.imview(x_gt, title="Ground truth", fig=fig, ax=ax[0])
plot.imview(y, title="Blurred, noisy image: %.2f (dB)" % metric.psnr(x_gt, y), fig=fig, ax=ax[1])
plot.imview(x, title="Deconvolved image: %.2f (dB)" % metric.psnr(x_gt, x), fig=fig, ax=ax[2])
fig.show()
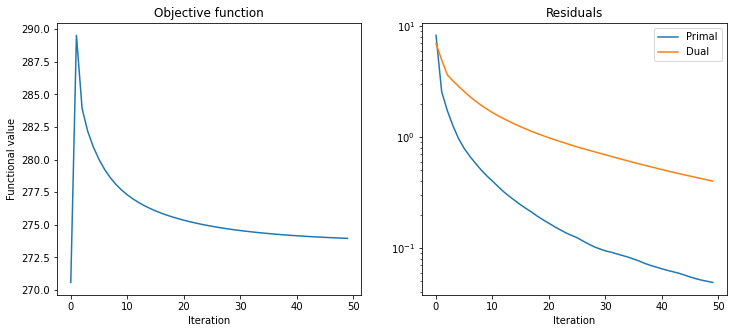
Plot convergence statistics.
[7]:
fig, ax = plot.subplots(nrows=1, ncols=2, figsize=(12, 5))
plot.plot(
hist.Objective,
title="Objective function",
xlbl="Iteration",
ylbl="Functional value",
fig=fig,
ax=ax[0],
)
plot.plot(
snp.vstack((hist.Prml_Rsdl, hist.Dual_Rsdl)).T,
ptyp="semilogy",
title="Residuals",
xlbl="Iteration",
lgnd=("Primal", "Dual"),
fig=fig,
ax=ax[1],
)
fig.show()