TV-Regularized Abel Inversion#
This example demonstrates a TV-regularized Abel inversion by solving the problem
\[\mathrm{argmin}_{\mathbf{x}} \; (1/2) \| \mathbf{y} - A \mathbf{x}
\|_2^2 + \lambda \| C \mathbf{x} \|_1 \;,\]
where \(A\) is the Abel projector (with an implementation based on a projector from PyAbel [24]), \(\mathbf{y}\) is the measured data, \(C\) is a 2D finite difference operator, and \(\mathbf{x}\) is the desired image.
[1]:
import numpy as np
import scico.numpy as snp
from scico import functional, linop, loss, metric, plot
from scico.examples import create_circular_phantom
from scico.linop.abel import AbelTransform
from scico.optimize.admm import ADMM, LinearSubproblemSolver
from scico.util import device_info
plot.config_notebook_plotting()
Create a ground truth image.
[2]:
N = 256 # image size
x_gt = create_circular_phantom((N, N), [0.4 * N, 0.2 * N, 0.1 * N], [1, 0, 0.5])
Set up the forward operator and create a test measurement.
[3]:
A = AbelTransform(x_gt.shape)
y = A @ x_gt
np.random.seed(12345)
y = y + np.random.normal(size=y.shape).astype(np.float32)
Compute inverse Abel transform solution.
[4]:
x_inv = A.inverse(y)
Set up the problem to be solved. Anisotropic TV, which gives slightly better performance than isotropic TV for this problem, is used here.
[5]:
f = loss.SquaredL2Loss(y=y, A=A)
λ = 2.35e1 # ℓ1 norm regularization parameter
g = λ * functional.L1Norm() # Note the use of anisotropic TV
C = linop.FiniteDifference(input_shape=x_gt.shape)
Set up ADMM solver object.
[6]:
ρ = 1.03e2 # ADMM penalty parameter
maxiter = 100 # number of ADMM iterations
cg_tol = 1e-4 # CG relative tolerance
cg_maxiter = 25 # maximum CG iterations per ADMM iteration
solver = ADMM(
f=f,
g_list=[g],
C_list=[C],
rho_list=[ρ],
x0=snp.clip(x_inv, 0.0, 1.0),
maxiter=maxiter,
subproblem_solver=LinearSubproblemSolver(cg_kwargs={"tol": cg_tol, "maxiter": cg_maxiter}),
itstat_options={"display": True, "period": 10},
)
Run the solver.
[7]:
print(f"Solving on {device_info()}\n")
solver.solve()
hist = solver.itstat_object.history(transpose=True)
x_tv = snp.clip(solver.x, 0.0, 1.0)
Solving on GPU (NVIDIA GeForce RTX 2080 Ti)
Iter Time Objective Prml Rsdl Dual Rsdl CG It CG Res
-----------------------------------------------------------------
0 2.78e+00 5.897e+04 3.479e+01 7.425e+01 17 9.734e-05
10 3.89e+00 5.973e+04 1.626e+00 6.635e-01 5 7.628e-05
20 3.96e+00 6.132e+04 8.589e-01 6.671e-02 0 8.422e-05
30 4.03e+00 6.182e+04 1.122e+00 2.967e-01 4 4.875e-05
40 4.10e+00 6.209e+04 5.846e-01 1.733e-01 4 8.004e-05
50 4.16e+00 6.224e+04 3.647e-01 2.823e-02 0 9.519e-05
60 4.23e+00 6.247e+04 7.896e-01 2.614e-01 3 4.133e-05
70 4.29e+00 6.259e+04 5.240e-01 3.870e-02 0 8.779e-05
80 4.38e+00 6.262e+04 3.133e-01 2.373e-02 0 9.670e-05
90 4.44e+00 6.266e+04 2.370e-01 5.154e-02 1 7.306e-05
99 4.49e+00 6.268e+04 2.341e-01 1.609e-02 0 9.352e-05
Show results.
[8]:
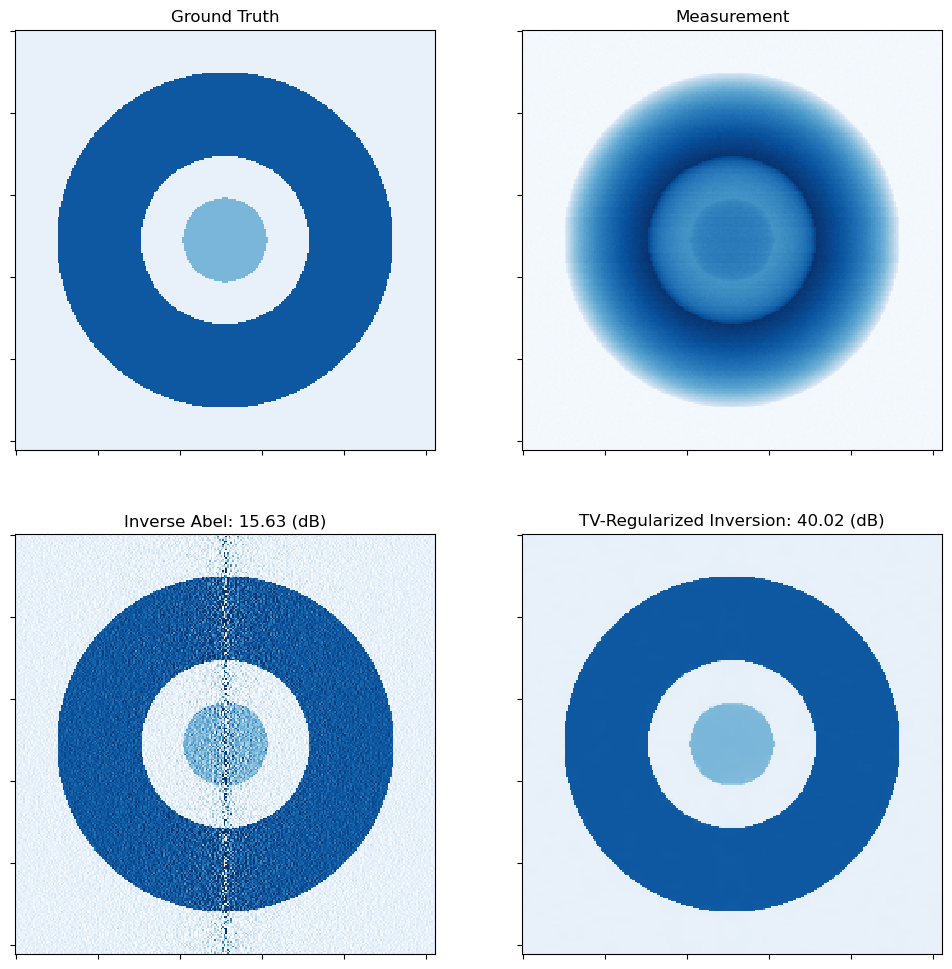
norm = plot.matplotlib.colors.Normalize(vmin=-0.1, vmax=1.2)
fig, ax = plot.subplots(nrows=2, ncols=2, figsize=(12, 12))
plot.imview(x_gt, title="Ground Truth", cmap=plot.cm.Blues, fig=fig, ax=ax[0, 0], norm=norm)
plot.imview(y, title="Measurement", cmap=plot.cm.Blues, fig=fig, ax=ax[0, 1])
plot.imview(
x_inv,
title="Inverse Abel: %.2f (dB)" % metric.psnr(x_gt, x_inv),
cmap=plot.cm.Blues,
fig=fig,
ax=ax[1, 0],
norm=norm,
)
plot.imview(
x_tv,
title="TV-Regularized Inversion: %.2f (dB)" % metric.psnr(x_gt, x_tv),
cmap=plot.cm.Blues,
fig=fig,
ax=ax[1, 1],
norm=norm,
)
fig.show()